By a miracle, it turns out the company ended up being rewarded a portion of their outstanding receivable balance they’d written off as part of the bankruptcy proceedings. Of the $50,000 balance that was written off, the company is notified that they will receive $35,000. Our credit risk assessment services also allow you to thoroughly evaluate customer creditworthiness and make informed decisions about whom to extend credit to.
Intermediate Financial Accounting II
A company can further adjust the balance by following the entry under the “Adjusting the retained earnings Allowance” section above. Bad Debt Expense increases (debit), and Allowance for Doubtful Accounts increases (credit) for $48,727.50 ($324,850 × 15%). To illustrate, let’s continue to use Billie’s Watercraft Warehouse (BWW) as the example.
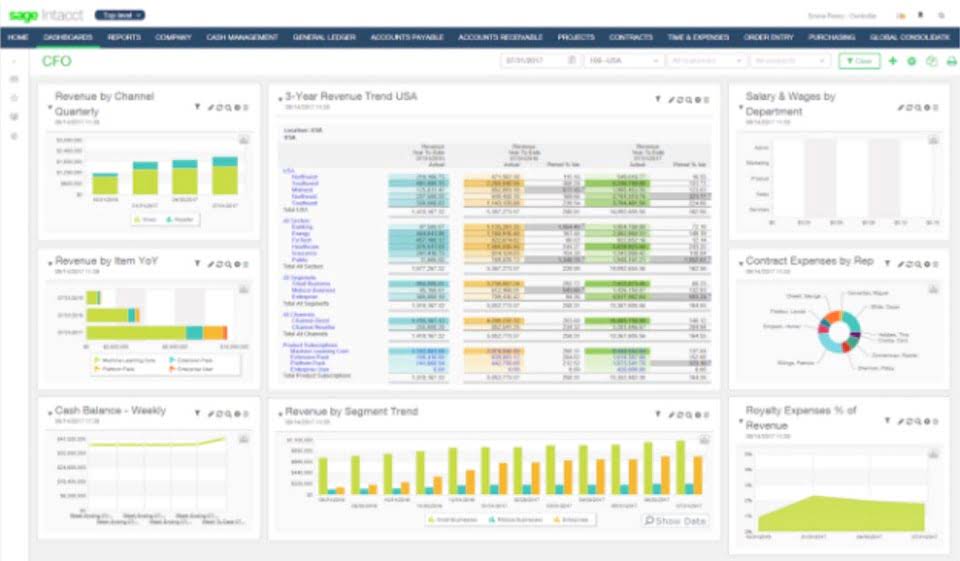
Balance Sheet Aging of Receivables Method for Calculating Bad Debt Expenses

Then all of the category estimates are added together to get one total estimated uncollectible balance for the period. The entry for bad debt would be as follows, if there was no carryover balance from the prior period. For example, when companies account for bad debt expenses in their financial statements, they will use an accrual-based method; however, they are required to use the direct write-off method on their income tax returns.
Historical Percentage Method
Assign a risk score to each customer, and assume a higher risk of default for those having a higher risk score. There are several possible ways to estimate the allowance for doubtful accounts, which are noted below. Note that if a company believes it may recover a portion of a balance, it can write off a portion of the account. To learn more about how we can help your business grow, contact one of our sales agents by filling out the form below.
Heating and Air Company
- Also note that it is a requirement that the estimation method be disclosed in the notes of financial statements so stakeholders can make informed decisions.
- The companies that qualify for this exemption, however, are typically small and not major participants in the credit market.
- However, if economic conditions decline in the current period, or management loosens the credit policy, then the bad debt rate in the current period will likely exceed what was experienced in prior periods.
- Auditors look for this issue by comparing the size of the allowance to gross sales over a period of time, to see if there are any major changes in the proportion.
- As such, effective credit management and debt collection procedures should be a critical part of the evaluation of how to limit the effect bad debt can have on your business.
- Bad Debt Expense increases (debit), and Allowance for Doubtful Accounts increases (credit) for $48,727.50 ($324,850 × 15%).
- The following entry should be done in accordance with your revenue and reporting cycles (recording the expense in the same reporting period as the revenue is earned), but at a minimum, annually.
The allowance, sometimes called a bad debt reserve, represents management’s estimate of the amount of accounts receivable that will not be paid by customers. The journal entry for the Bad Debt Expense increases (debit) the expense’s balance, and the Allowance for Doubtful Accounts increases (credit) the balance in the Allowance. The allowance for doubtful accounts is a contra asset account and is subtracted from Accounts Receivable to determine the Net Realizable Value of the Accounts Receivable account on the balance sheet. In the case of the allowance for doubtful accounts, it is a contra account that is used to reduce the Controlling account, Accounts Receivable. The company can recover the account by reversing the entry above to reinstate the accounts receivable balance and the corresponding allowance for the doubtful account balance. Then, the company will record a debit to cash and credit to accounts receivable when the payment is collected.
- The entry for bad debt would be as follows, if there was no carryover balance from the prior period.
- An allowance for doubtful accounts is a contra account that nets against the total receivables presented on the balance sheet to reflect only the amounts expected to be paid.
- If a company is using the accrual basis of accounting, it should record an allowance for doubtful accounts, since it provides an estimate of future bad debts that improves the accuracy of the company’s financial statements.
- The projected bad debt expense is properly matched against the related sale, thereby providing a more accurate view of revenue and expenses for a specific period of time.
- That total is reported in Bad Debt Expense and Allowance for Doubtful Accounts, if there is no carryover balance from a prior period.
- This is because the expense was already taken when creating or adjusting the allowance.
How to Estimate the Allowance for Doubtful Accounts

All categories of estimated uncollectible amounts are summed to get a total estimated uncollectible balance. That total is reported in Bad Debt Expense and Allowance for Doubtful Accounts, if there is no carryover balance from a prior period. If there is a carryover balance, that must be considered before recording Bad Debt Expense. The balance sheet aging of receivables method is more complicated than the other two methods, but it tends to produce more accurate results. The balance sheet method (also known as the percentage of accounts receivable method) estimates bad debt expenses based on the balance in accounts receivable. The method looks at the balance of accounts receivable at the end of the period and assumes that a certain amount will not be collected.
In accordance with the matching principle of accounting, this ensures that expenses related to the sale are recorded in the same accounting period as the revenue is earned. The allowance for doubtful accounts also helps companies more accurately estimate the actual value of their account receivables. The allowance for doubtful accounts is a reduction of the total amount of accounts receivable appearing on a company’s balance sheet. This deduction is classified as a contra asset account, so it is paired with and offsets the accounts receivable line item.

Estimation by Risk Classification
Based on previous experience, 1% of accounts receivable less than 30 days old will be uncollectible, and 4% of the allowance for doubtful accounts is a contra asset account that equals those accounts receivable at least 30 days old will be uncollectible. Accountants use allowance for doubtful accounts to ensure that their financial statements accurately reflect the current state of their receivables. Management may disclose its method of estimating the allowance for doubtful accounts in its notes to the financial statements. Some companies may classify different types of debt or different types of vendors using risk classifications.
Specific Identification Method
In accrual-basis accounting, recording the allowance for doubtful accounts at the same time as the sale improves the accuracy of financial reports. The projected bad debt expense is properly matched against the related sale, thereby providing a more accurate view of revenue and expenses for a specific period of time. In addition, this accounting process prevents the large swings in operating results when uncollectible accounts are written off directly as bad debt expenses. If a company is using the accrual basis of accounting, it should record an allowance for doubtful accounts, since it provides an estimate of future bad debts that improves the accuracy of the company’s financial statements. If a certain percentage of accounts receivable became bad debts in the past, then use the same percentage in the future. This approach can work well when economic conditions persist over several years, so that loss rates can be expected to persist over time.
 Italiano
Italiano
Leave a Reply