When calculating the replacement cost of an asset, a company must account for depreciation costs. A business capitalizes an asset purchase by posting the cost of a new asset to an asset account, and the asset account is depreciated over the asset’s useful life. The cost of the asset includes all costs to prepare the asset for use, such as insurance costs and the cost of setup. Furthermore, the cost approach is of particular importance for the valuation of the workforce—a key component of a firm’s goodwill and a crucial input for the income approach, particularly when using the multi-period excess earnings method. This means that rca is more accurate when compared to cpp because it calculates Depreciation on the basis of current costs rather than historical costs. Several problems arise from the current valuation standards and guidance in relation to the gross sales vs net sales: key differences explained and they can be classified as definitional and methodological.
To Ensure One Vote Per Person, Please Include the Following Info
The concept is also used in capital budgeting, when formulating estimates of the funding needed to replace existing assets as they wear out. A business might even set aside cash for several years prior to actually replacing a major asset, based on the amount of its estimated replacement cost. The first step in the replacement Cost Accounting process is to identify all Fixed Assets and their corresponding original purchase price and index number. The second step is to calculate Depreciation on an annual basis, using either the historical cost or current purchasing power methodologies. In business, a replacement cost is the cost of restoring or replacing an asset that has been sold or damaged. This may be different from the cash value of that asset, due to factors like depreciation and market fluctuations.
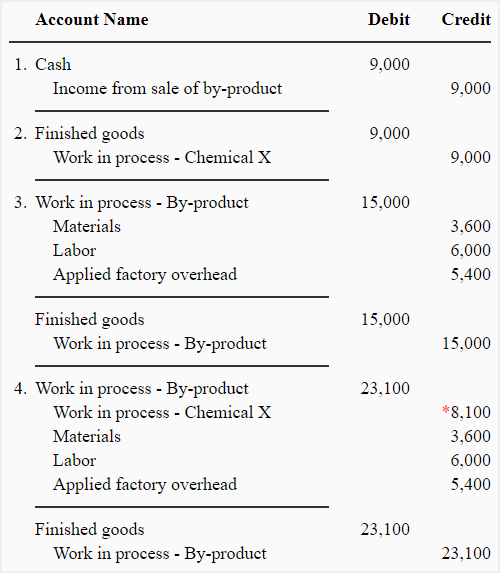
4 Valuation approaches, techniques, and methods
Let’s delve into what replacement cost entails, its applications, and how it influences decision-making in various contexts. Replacement cost is the price that an entity would pay to replace an existing asset at current market prices with a similar asset. If the asset in question has been damaged, then the replacement cost relates to the pre-damaged condition of the asset. Replacement cost is a term referring to the amount of money a business must currently spend to replace an asset like a fixture, a machine, a vehicle, or an equipment, at current market prices. Sometimes referred to as a “replacement value,” a replacement cost may fluctuate, depending on factors such as the market value of components used to reconstruct or repurchase the asset and the expenses involved in preparing assets for use. The replacement cost technique is beneficial for those who can take advantage of the same.
What is a replacement cost accounting?
For example, a manufacturer of precision widgets knows that a widget lathe will wear out in three years, and so develops a plan for how to come up with its $30,000 expected replacement cost. When the lathe wears out, the manufacturer will have the money to buy a new one. Replacement cost can also be used to estimate the amount of funding that might be required to duplicate another business. This concept can be used to establish one of several possible price points that can be used in the formulation of a proposed price to pay the shareholders of a target company as part of an acquisition. The company should make a wise decision by carefully calculating this cost by comparing its repair and maintenance costs, which can be levied over the years if the asset is not replaced. Replacement cost is the cost involved in replacing an existing item with another item having same or similar features.
Do you own a business?
The total depreciation expense recognized over the asset’s useful life is the same, regardless of which method is used. As part of the process of determining what asset is in need of replacement and what the value of the asset is, companies use a process called net present value. To make a decision about an expensive asset purchase, companies first decide on a discount rate, which is an assumption about a minimum rate of return on any company investment.

What is your current financial priority?
- The policy is designed so that the policyholder gets some benefit from the insurance companies.
- Actual cash value refers to the monetary value of the property, measured as replacement cost minus depreciation.
- Once an asset is purchased, the company determines a useful life for the asset and depreciates the asset’s cost over the useful life.
- The cost of the asset includes all costs to prepare the asset for use, such as insurance costs and the cost of setup.
- Understanding these distinctions is crucial for accurate and comprehensive property valuation.
Price level change can be a problem when attempting to charge depreciation on fixed assets. These materials were downloaded from PwC’s Viewpoint (viewpoint.pwc.com) under license. A positive difference signifies the asset’s profitability, allowing the company to proceed with the purchase.
This budget is essential for planning future asset acquisitions and determining how the company will generate cash inflows to cover the costs of new assets. Company currently owns a Truck with a net book value of $ 40,000 as it has been depreciating by 60% since the purchase date. Management asks the accountant to calculate the depreciated replacement cost of this Truck. Depreciated replacement cost of an asset is the current cost to replace the asset less accumulated depreciation. It is the cost company spends to acquire the current replacement asset and deduct the accumulated depreciation to reflects with the current asset condition. It is simply the replacement cost less depreciation which already deduct from current asset.
They are distinctly different concepts that are estimated using different criteria. It is not necessary that the market value and replacement cost of a building are identical, as the two are distinctly different approaches to valuing a property using real estate data analytics. The accountant has contacted suppliers, the current market price of the same truck is $ 120,000, the price increase due to high demand. Insurance policies have a great role to play in the working of the replacement value.
Make the necessary adjustment in the ledger using the index number and replacement cost. The aim of depreciation is to ensure that the profit and loss account is in order and to make a provision for the replacement of the fixed asset after long-term use. As a graduate of Eastern University in Business Administration, I have gained significant knowledge insurance. Replacement cost excludes additional expenses like demolition, debris removal, and site accessibility premiums. This factors in land value, site improvements, and subtracting accrued depreciation. Depreciation aligns the revenue earned from using the asset with the expense of its usage over time.
Some assets undergo straight-line depreciation, dividing the cost by the useful life to determine the annual depreciation. The cost of the asset encompasses all expenses related to preparing it for use, including insurance costs and setup expenses. To compare market value to replacement cost, adjustments must be made for such factors. When comparing market value to replacement cost, it is important to understand what both represent and what factors are considered in each circumstance. Our mission is to empower readers with the most factual and reliable financial information possible to help them make informed decisions for their individual needs. Finance Strategists is a leading financial education organization that connects people with financial professionals, priding itself on providing accurate and reliable financial information to millions of readers each year.
 Italiano
Italiano
Leave a Reply