
On a company’s balance sheet, retained earnings or accumulated deficit balance is reported in the stockholders’ equity section. Stockholders’ equity is the amount of capital given to a business by its shareholders, plus donated capital and earnings generated by the operations of the business, minus any dividends issued. Retained earnings refer to the portion of a company’s net income or profits that it retains and reinvests in the business instead of paying out as dividends to shareholders. It’s an equity account in the balance sheet, and equity is the difference between assets (valuables) and liabilities (debts). The amount of retained earnings is calculated by subtracting total dividends paid to shareholders from the total net income in a fiscal year.
Step 1: Prepare the Statement Heading
Alternatively, companies take the net income for the period to the retained earnings account first. Subsequently, they subtract any declared dividends from that balance. Because expenses have yet to be deducted, revenue is the highest number reported on the income statement.
- During a specific financial period, it reports the business’s revenue, liabilities, and numbers for the shareholders’ equity section.
- This document is essential as you learn how to calculate retained earnings and other equities.
- It reveals the “top line” of the company or the sales a company has made during the period.
- At the end of every year, the company’s net income gets rolled into retained earnings.
- Use a retained earnings account to track how much your business has accumulated.
What Factors Impact Retained Earnings?
- This is the net profit or loss figure from the current accounting period, from which the retained earnings amount is calculated.
- For traded securities, an ex-dividend date precedes the date of record by five days to permit the stockholder list to be updated and serves effectively as the date of record.
- In this case, dividends can be paid out to stockholders, or extra cash might be put to use.
- If a company sells a product to a customer and the customer goes bankrupt, the company technically still reports that sale as revenue.
- In contrast, when a company suffers a net loss or pays dividends, the retained earnings account is debited, reducing the balance.
Like in a general partnership, profits of an LLC are generally distributed to the shareholders. Any profits that are not distributed at the end of the LLC’s tax year are considered retained earnings. Retained earnings, on the other hand, specifically refer to the portion of a company’s profits that remain within the business instead of being distributed to shareholders as dividends. Net profit refers to the total revenue generated by a company minus all expenses, taxes, and other costs incurred during a given accounting period. If a business sold all of its assets and used the cash to pay all liabilities, the https://www.bookstime.com/ leftover cash would equal the equity balance.

Ask a Financial Professional Any Question

A statement of retained earnings details the changes in a company’s retained earnings balance over a specific period, usually a year. Positive retained earnings signify financial stability and the ability to reinvest in the company’s growth. This usually gives companies more options to fund expansions and other initiatives without relying on high-interest loans or other debt. Retained earnings, at their core, are the portion of a company’s net income that remains after all dividends and distributions to shareholders are paid out. Shareholder’s equity section includes common stock, additional paid-in capital, and retained earnings.

The funds are used net sales to pay shareholders in the form of dividends or compensation, and while they are not considered assets of the company, they are an additional equity shareholder capital. While retained earnings are not classified as current liabilities, they can still affect a company’s current liabilities. Retained earnings may be used to acquire new assets, pay off debts, or finance operations.
- Retained earnings are the cumulative profit and losses of a company that has been reinvested into the business rather than being distributed as dividends to shareholders.
- Retained earnings, however, are not considered current liabilities.
- Liabilities are obligations that must be paid, while assets are resources that can be used to generate value.
- Similarly, any of these obligations that companies must repay within 12 months are current liabilities.
- On the balance sheet, retained earnings appear under the “Equity” section.
- Net Income is the profit your company made during the current period after all expenses have been deducted from revenues.
- Retained earnings accumulate all profits and losses from when a company starts operating.
Is Owners Equity and Retained Earnings the Same Thing?
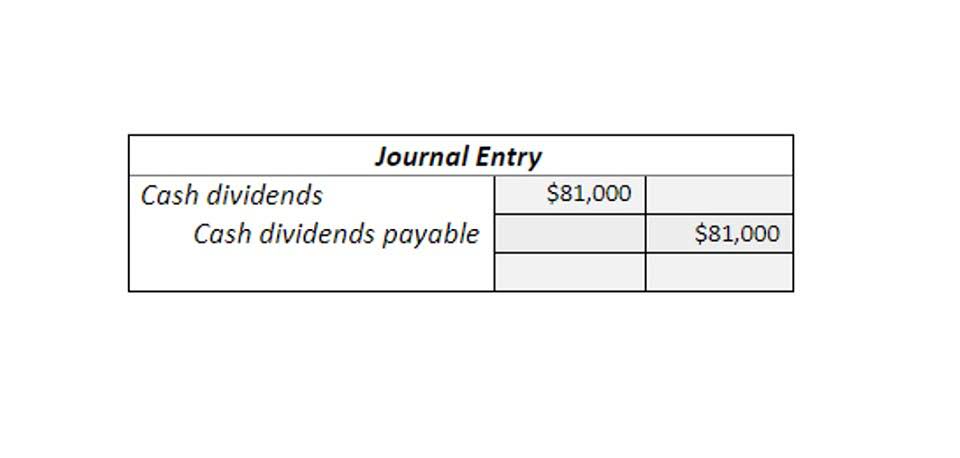
Retained earnings at the beginning of the period are actually the previous year’s retained earnings. This can be found in the balance of the previous year, under the shareholder’s equity section on the liability side. In our example, December 2023 is the current year for which retained earnings need to be calculated, so December 2022 would be the previous year. Meaning the retained earnings balance as of December 31, 2022 would be the beginning period retained earnings for the year 2023. Retained earnings are calculated by adding/subtracting, the current year’s net profit/loss, to/from the previous year’s retained earnings, then subtracting dividends paid in the current year from the same.
Do you own a business?
Retained earnings are an equity balance and as such are included within the equity section of a company’s balance are retained earnings a current liability sheet. You must adjust your retained earnings account whenever you create a journal entry that raises or lowers a revenue or expense account. If you are a new business and do not have previous retained earnings, you will enter $0. And if your previous retained earnings are negative, make sure to correctly label it.
 Italiano
Italiano
Leave a Reply